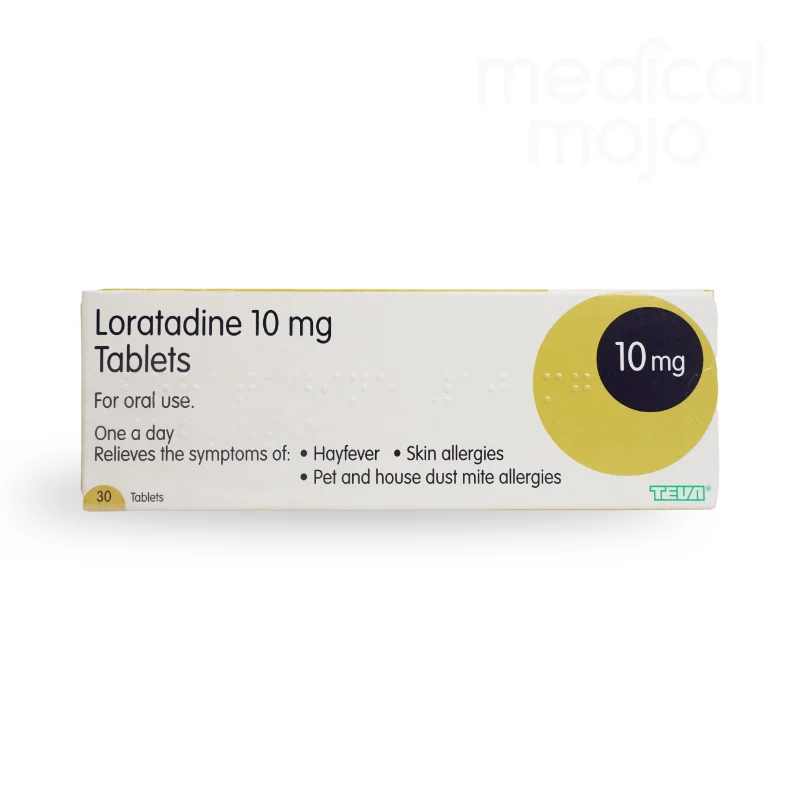
What are Loratadine Tablets?
Loratadine tablets are an antihistamine medication that can be taken by both adults and children aged 2 years and older to treat symptoms caused by mild to moderate allergic conditions. This non-drowsy antihistamine is taken once a day to prevent the body's inflammatory reaction to allergens.
What is Loratadine used for?
Loratadine tablets are used to treat the symptoms of various allergies, including:
- Hay fever
- Skin reactions like hives
- Allergies caused by pets and dust mites
- Insect bites and stings
- Mild food allergies
The symptoms that Loratadine can help alleviate include:
- Sneezing
- Runny nose
- Itchy nose and throat
- Itchy and watery eyes
- Itchy skin and rashes
How does Loratadine work?
Loratadine is an antihistamine that works by blocking the effects of histamine, a substance that your body produces during an allergic reaction. Histamine is responsible for causing inflammation and irritation in the eyes, nose, and skin. By preventing histamine from binding to its receptors, Loratadine helps to reduce and prevent these allergic symptoms.
Can you take Loratadine and Cetirizine together?
Both Loratadine and Cetirizine are non-drowsy antihistamines that work in a similar way to reduce allergy symptoms. However, they should not be taken together within a 24-hour period unless advised by a doctor, as both medications are designed to be taken once a day.
What is the difference between Loratadine and Cetirizine?
While both Loratadine and Cetirizine are long-acting, non-drowsy antihistamines, they may have different side effects. Cetirizine is more commonly associated with:
- Nausea
- Jitteriness
- Sore throat
- Drowsiness
Loratadine, on the other hand, may cause:
- Nervousness
- Disturbed sleep
Is Loratadine or Cetirizine better for itching?
Both Loratadine and Cetirizine are effective for treating itchy skin caused by allergic conditions. There is no definitive research suggesting that one is more effective than the other, though individual responses may vary.
What is Desloratadine, and how does it compare to Loratadine?
Desloratadine is a non-drowsy antihistamine and the active metabolite of Loratadine, meaning it is what remains after Loratadine is processed by the body. Desloratadine is used similarly to Loratadine for treating allergy symptoms affecting the eyes, nose, mouth, and skin. One notable difference is that Desloratadine can be used in children as young as 1 year old, whereas Loratadine is only approved for children over 2 years old.
Does Loratadine make you drowsy?
Loratadine is classified as a non-sedating antihistamine, meaning it is less likely to cause drowsiness compared to older antihistamines. However, in some cases, it may still cause drowsiness, so it's advisable to wait until you know how it affects you before driving or operating machinery.
What is the recommended dosage of Loratadine?
For children and adults over 2 years old who weigh over 20 kg, the recommended dose is one 10 mg tablet once a day. The tablet should be taken orally with a glass of water.
What should you do if you overdose on Loratadine?
You should only take Loratadine as directed in the Patient Information Leaflet. If you take more than the recommended dose, you may experience unwanted side effects and should seek medical advice immediately.
What are the possible side effects of Loratadine?
Common side effects in adults and children over 12 years old include:
- Drowsiness
- Headache
- Increased appetite
- Difficulty sleeping
In children aged 2 to 12 years, the most common side effects are:
- Headache
- Nervousness
- Tiredness
Very rare side effects (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people) include:
- Dizziness
- Seizures
- Fast or irregular heartbeat
- Nausea
- Dry mouth
- Upset stomach
- Liver problems
- Hair loss
- Tiredness
What are the warnings for Loratadine?
Before taking Loratadine tablets, make sure to read and understand all warnings and precautions listed in the Patient Information Leaflet. You should consult your doctor or pharmacist if:
- You have a liver condition, as you may need a lower dose.
- You have recently taken or are currently taking any other prescribed or non-prescribed medication.
- You are due to undergo a skin prick test for allergies, as Loratadine should not be taken for 2 days before the test to avoid affecting the results.
Is Loratadine safe to take during pregnancy and breastfeeding?
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, consult your doctor or pharmacist before taking Loratadine. It is generally recommended to avoid using Loratadine during pregnancy and breastfeeding unless advised by a healthcare professional.
Can you drink alcohol while taking Loratadine?
It is not recommended to drink alcohol while taking Loratadine, as it may increase the risk of drowsiness.